Does Britain Work More Hours Than The Rest Of The World/Europe/America?

In today’s fast-paced global economy, a common question that arises is, “how many hours do employees in different countries work?” This blog delves into the intriguing world of work hours, comparing how employees across various nations, from the bustling cities of Western Europe to the vibrant coasts of Australia, dedicate time to their main job. We’ll explore the intricacies of the working week, examining the average hours employees worked in key countries like France and Germany, and venturing beyond to see how hours in the EU stack up against those in other parts of the world.
Our journey will also take us to the U.S. and Australia, shedding light on how Americans and Australians worked their week on average, and offering a comprehensive view of work cultures globally. This exploration is not just about numbers; it’s a window into the diverse work-life balances and economic structures shaping lives around the world. Join us as we navigate through this fascinating comparison of work hours, uncovering what a typical week looks like for workers in different corners of the globe.
Quick Links:
- The UK’s Working Hours In A Global Context
- Britain And Europe – A Comparative Analysis
- The UK vs America – A Work Culture Contrast
- Factors Influencing Average Working Hours In The UK
- Work-Life Balance – How Does The UK Fare?
- Average Annual Working Hours FAQs
Highlights And Key Takeaways:
- The average working hours per week are fewer for UK full time workers (36.4) compared to the average hours worked in European countries (37.5).
- Salaried employees in the U.S. and UK work the same amount of hours a week, although U.S.
- Of the 37 member countries of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), the average number of hours worked by a full-time employee is 36, positioning the UK just above this statistic.
The UK’s Working Hours In A Global Context
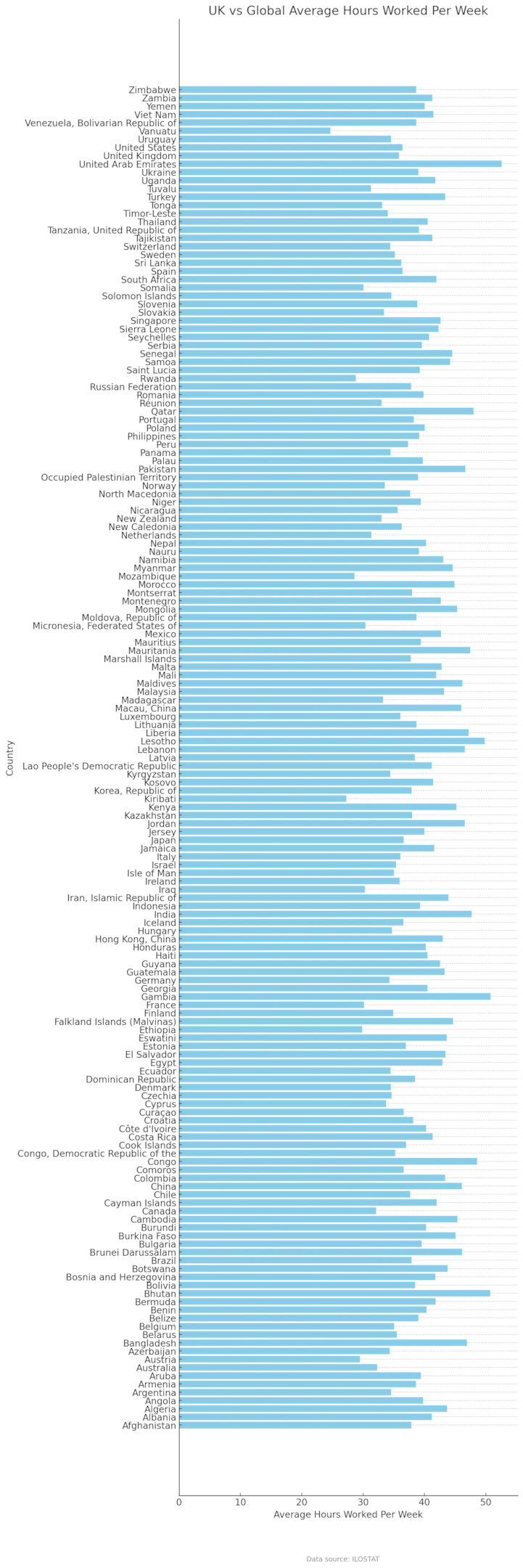
An examination of the average working hours in the United Kingdom, especially in the context of global statistics, offers an insightful perspective on work cultures and economic conditions worldwide. According to data from the International Labour Organization ILOSTAT, the UK’s average working hours per week stand at a moderate level when compared globally.
Overview of Average Working Hours in the UK
As per the data, the UK’s average working hours per week are 36.4. This figure places the UK in a moderate position on the global scale, reflecting a balanced approach to work-life integration. This conclusion is corroborated by data from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), highlighting the average hours a week worked by a full-time employee as 36.
Comparison with Global Statistics
- Regions with the Longest Working Hours: Countries like Algeria (43.7 hours per week) and Albania (41.21 hours) exhibit some of the longest working hours. These extended hours can be attributed to various factors, including economic demands and local work cultures that prioritise long working hours.
- Regions with the Shortest Working Hours: On the other end of the spectrum, countries like Argentina (34.55 hours) and Afghanistan (37.85 hours) have shorter working hours. The shorter hours in these regions might be influenced by different socio-economic contexts and labour regulations.
Factors Contributing to These Differences
- Cultural Norms: The work culture in each country significantly impacts the average working hours. In some countries, there’s a cultural emphasis on working longer hours as a sign of commitment and productivity, while in others, there’s a greater focus on work-life balance.
- Economic Conditions: The economic structure and level of development in a country also play a crucial role. In developing economies, longer hours might be necessary to meet economic needs, whereas in more developed countries, there’s often a shift towards shorter, more productive working hours.
- Labour Regulations: Government policies and labour laws greatly influence working hours. Countries with stringent labour laws often have shorter working hours and better work-life balance, while those with less regulation might see longer working hours.
In conclusion, the UK’s average working hours place it in a moderate position globally. The variations in working hours across different regions are influenced by a complex interplay of cultural norms, economic conditions, and labour regulations. Understanding these factors is key to comprehending the global context of working hours and the position of the UK within it.
Britain And Europe – A Comparative Analysis
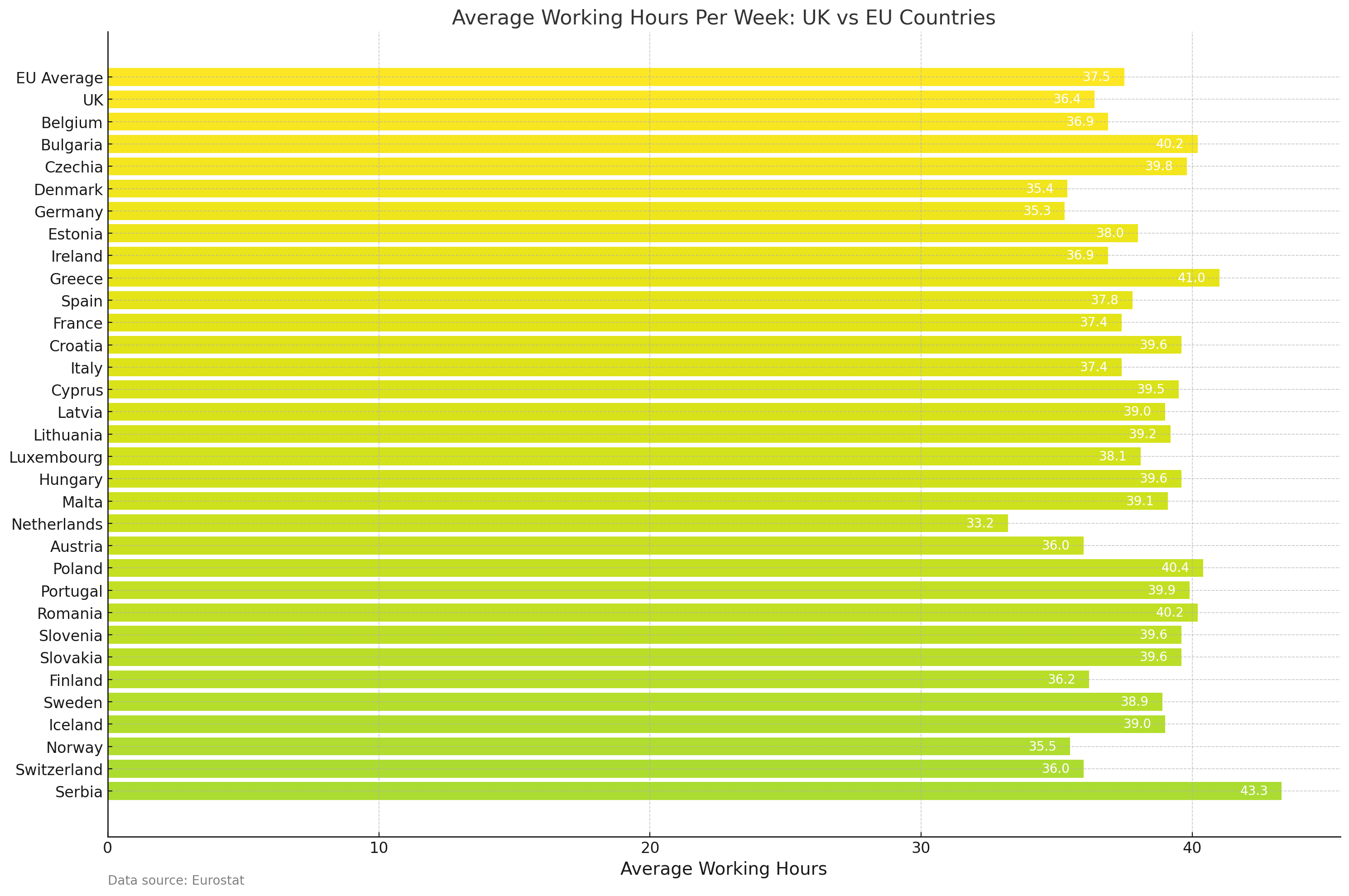
In examining the working hours of the United Kingdom in relation to its European counterparts, a fascinating tapestry of work cultures and norms emerges. Based on the ONS and eurostat data (employed persons 20-64), the average working hours per week in the UK are 36.4 hours. This places the UK in a moderate position compared to other European countries.
Comparing the UK with European Countries
- Countries with Longer Working Hours: Notably, countries like Greece (41.0 hours), Romania and Bulgaria (both at 40.2 hours), and Poland (40.4 hours) surpass the UK in terms of longer working hours. Serbia stands out with an average of 43.3 hours per week, significantly higher than the UK. This could be reflective of differing economic needs and workplace regulations.
- Countries with Shorter Working Hours: On the other end of the spectrum, Denmark (35.4 hours) and Germany (35.3 hours) report shorter working hours than the UK. The Netherlands notably reports the shortest working hours in Europe, at 33.2 hours per week. These differences can be attributed to stronger emphasis on work-life balance and efficient work practices.
UK in the Context of the European Union
The average working hours for the 27 countries of the European Union is 37.5 hours, slightly higher than the UK’s average. This places the UK below the EU average, suggesting a comparatively better balance between work and leisure.
Impact of the EU’s Working Time Directive
The European Union’s Working Time Directive plays a crucial role in shaping work hours across Europe. This directive sets limits on working hours, mandating a maximum of 48 hours per week, including overtime.
The UK’s alignment with these standards, despite having slightly shorter average working hours than the EU average, demonstrates the country’s commitment to maintaining a balance between the demands of the workforce and the well-being of its workers. However, the variations among countries indicate that national policies, cultural attitudes towards work, and economic structures significantly influence the adherence and impact of the EU directive. You can read further on Working Time Regulations and the Working Time Directive, in our guide – UK Employment Hours: A Comprehensive Guide To Work Hours.
In conclusion, while the UK does not have the longest working hours in Europe, it maintains a moderate position. The EU’s working time directive provides a framework, but national differences highlight the complexity of work cultures across Europe. This comparative analysis reveals a diverse landscape of working hours, reflecting the unique economic and social fabrics of each country.
The UK vs America – A Work Culture Contrast

In an intriguing comparison between the work cultures of the United Kingdom and the United States, we find that the average working hours per week are remarkably similar, with the UK at 36.4 and the U.S. at 36.43 hours, as per data from the ONS and the International Labour Organization, respectively. However, this numerical similarity masks deeper differences in work culture and practices.
Comparison of Average Working Hours
Despite the nearly identical average working hours, the context in which these hours are worked differs significantly between the two nations. This contrast is particularly evident when considering factors like work intensity, flexibility, and the nature of job roles.
Impact of Statutory Holidays and Annual Leave
A major differentiating factor is the approach to statutory holidays and annual leave. The UK mandates a minimum of 28 days of paid leave (including public holidays), fostering a culture where taking full leave is normalised.
In contrast, the U.S. does not have federal laws mandating paid leave or public holidays. This often results in fewer days off for American workers, potentially leading to longer total annual working hours despite the similarity in weekly averages.
Workplace Culture and Expectations
American workplace culture is often characterised by a strong emphasis on career success and longer work hours, sometimes leading to a ‘work-first’ mentality. This can manifest in expectations of availability outside of standard working hours and a tendency towards working longer to demonstrate commitment.
The UK work culture, while also valuing professionalism and career progression, tends to place greater emphasis on achieving a work-life balance. This is reflected in more widespread acceptance of flexible working arrangements and a general expectation that employees should take their full annual leave entitlement. The perception and management of overtime also differ. In the UK, there are more stringent regulations around overtime, while in the U.S., unpaid overtime is not uncommon, especially for salaried positions.
While the average working hours in the UK and U.S. are strikingly similar, the approach to work-life balance, annual leave, and overall workplace expectations reveals a notable contrast. The UK’s framework offers more statutory protections for workers’ time off, whereas the U.S. work culture often prioritises career and work, sometimes at the expense of personal time. This comparative analysis shows that understanding work culture requires looking beyond just the number of hours worked and considering the broader social and legal context in which these hours are set.
Factors Influencing Average Working Hours In The UK

In the United Kingdom, the typical working week is defined by a multitude of factors, ranging from industry-specific norms to broader economic and regulatory influences. Understanding these factors helps in comprehending how the average working hours in the UK are shaped and influenced.
Industry Type and Sector Variations
The UK’s diverse economic landscape means that working hours can vary significantly across different sectors. For instance, industries like finance and tech might demand longer hours due to project deadlines and global market hours, while public sector roles often adhere to more standardised working times. Our blog, Do Average Hours Vary In Different Sectors?, delves deeper into this topic, offering insights into how different industries in the UK operate in terms of working hours.
Employee Rights and Economic Demands
Employee rights in the UK, such as the right to a maximum 48-hour working week (opt-out available), minimum rest periods, and paid leave, play a crucial role in shaping average working hours. These rights ensure a balance between the demands of the job and the well-being of workers.
Economic demands also influence working hours. In times of economic prosperity or high demand, industries may experience an uptick in working hours. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to reduced hours or increased part-time employment.
The Role of Remote and Flexible Working Trends
The recent shift towards remote and flexible working has had a significant impact on working hours in the UK. This trend, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has introduced greater flexibility in work schedules, allowing employees to better manage their time and work commitments. This shift is not only changing where we work but also when and how we work, as discussed in our blog, Average Working Hours In The UK.
Government Policies and Regulations
UK government policies and employment regulations play a pivotal role in setting the framework for working hours. This includes legislation around minimum wage, overtime pay, and employment contracts. The importance of understanding these legal frameworks for both employers and employees is highlighted in our comprehensive guide, The Hiring Blueprint: UK Contract Of Employment Template. This resource is crucial for navigating the complexities of employment agreements and ensuring compliance with legal standards.
Emphasising Clarity and Detail in Job Listings
To optimise your recruitment process, it’s crucial to employ a UK job description template or job advert template that meticulously details the nature of the role – specifically, whether it’s full-time or part-time, and the anticipated number of working hours. This level of precision in your job advertisements and job descriptions, not only streamlines the hiring procedure but also guarantees that prospective applicants have a comprehensive grasp of what the position entails. This upfront clarity is key in attracting the right talent and setting clear expectations from the start.
In summary, the average working hours in the UK are influenced by a dynamic mix of industry norms, employee rights, economic conditions, and the evolving landscape of remote and flexible work. Government policies and regulations provide the foundational structure within which these factors operate. Understanding these elements is key to navigating the UK’s working environment, whether as an employer or an employee. For more in-depth analysis and practical guidance, our employment blogs offer valuable resources and insights into the nuances of working hours in different sectors and the legal frameworks governing employment in the UK.
Work-Life Balance – How Does The UK Fare?

The concept of work-life balance in the United Kingdom has evolved significantly over the past decade, reflecting changes in societal values, workplace norms, and government policies. Balancing the demands of work with personal life, especially in an era of long hours and heightened economic pressures, remains a central issue for UK workers.
The UK’s Work-Life Balance in the Global Context
When compared to other developed countries, the UK’s approach to work-life balance exhibits both strengths and challenges. Official statistics suggest that while the average UK worker tends to work shorter hours than the average US worker, they still work longer than their counterparts in several European countries.
The emphasis on long hours in the UK, especially in certain sectors, has often been associated with less time for personal life, impacting relationships with family and friends. However, there is a growing recognition that productivity is not solely dependent on the number of hours worked.
Comparative Analysis with Other Countries
Studies indicate that work-life balance satisfaction varies widely. In countries where working shorter hours is the norm, employees often report higher satisfaction in balancing work and life. In contrast, countries with a culture of working long hours, including the UK, show a need for improvement in this area.
The UK’s work-life balance is undergoing a transition, influenced by changing attitudes towards productivity and the importance of personal time. This shift is more pronounced when compared to countries like the US, where longer working hours are more deeply ingrained in the work culture.
Initiatives and Policies in the UK
The UK has introduced several initiatives and policies aimed at enhancing work-life balance. Notable among these is the improved parental leave policy, allowing parents to spend more time with their children without the pressure of work. Flexible working arrangements have become increasingly popular in the UK, with many companies adopting policies that allow for varied hours and remote working, helping employees to manage their time more effectively.
The government and various organisations are promoting the concept that productivity should be measured by output rather than just hours spent at work. This shift in mindset is encouraging companies to focus on efficiency and effectiveness, rather than just getting employees to work longer.
In summary, while the UK has made strides in improving work-life balance, there remains room for growth, especially when compared to other developed countries. The move towards policies that favour shorter hours, flexibility, and a focus on productivity over long hours, is a positive step towards achieving a better work-life balance for UK workers. As societal attitudes continue to evolve, it is likely that the UK will continue to refine its approach to balancing the demands of work and the needs of employees’ personal lives.
Average Annual Working Hours FAQs
Next, we tackle any remaining questions you may have on how UK average annual working hours compare to other countries:
DOES THE UK WORK THE LONGEST HOURS IN EUROPE?
The United Kingdom, while known for a robust work culture, does not typically hold the record for the longest working hours in Europe. This distinction often goes to countries in Southern or Eastern Europe, where work weeks can be longer. However, it’s crucial to distinguish between official working hours and actual hours worked, as cultural norms and individual industries can significantly influence these figures.
On average, American workers tend to log more hours than their British counterparts. This is partly due to differences in workplace cultures and regulations regarding work hours and holidays. The United States has fewer statutory holiday entitlements compared to the UK, contributing to longer working hours annually.
Countries with the longest working hours often vary year to year and are typically found in Asia or the Middle East. For instance, South Korea and Mexico have been noted for their particularly long working hours. These lengthy hours are influenced by cultural norms, economic demands, and in some cases, limited regulatory frameworks regarding work-life balance.
Within the European Union, countries like Greece and Poland have been observed to have the highest average working hours. These longer hours can be attributed to various factors, including economic conditions, labour laws, and cultural attitudes towards work.



